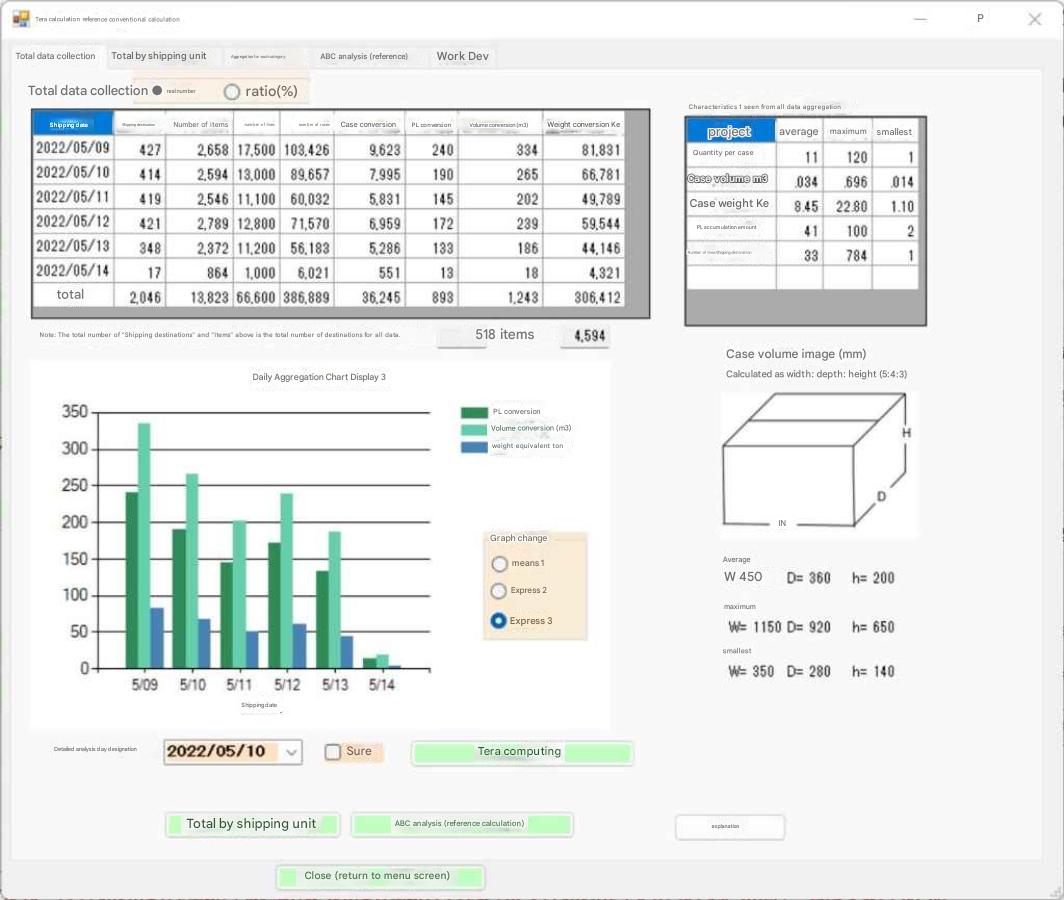
出荷データにはケース容積データはあるがケース寸法の概念がない。
「ケース容積イメージ」は縦5、横4、高さ3の比率でケース寸法をイメージしている。
ケース容積を算出しているということは、別データとしてケース寸法データは有るので、ケース寸法データと出荷データをリンクすればアイテム個々の寸法を解る。Tera計算ではケース寸法データが手元に無いとしてケース寸法を推定している。
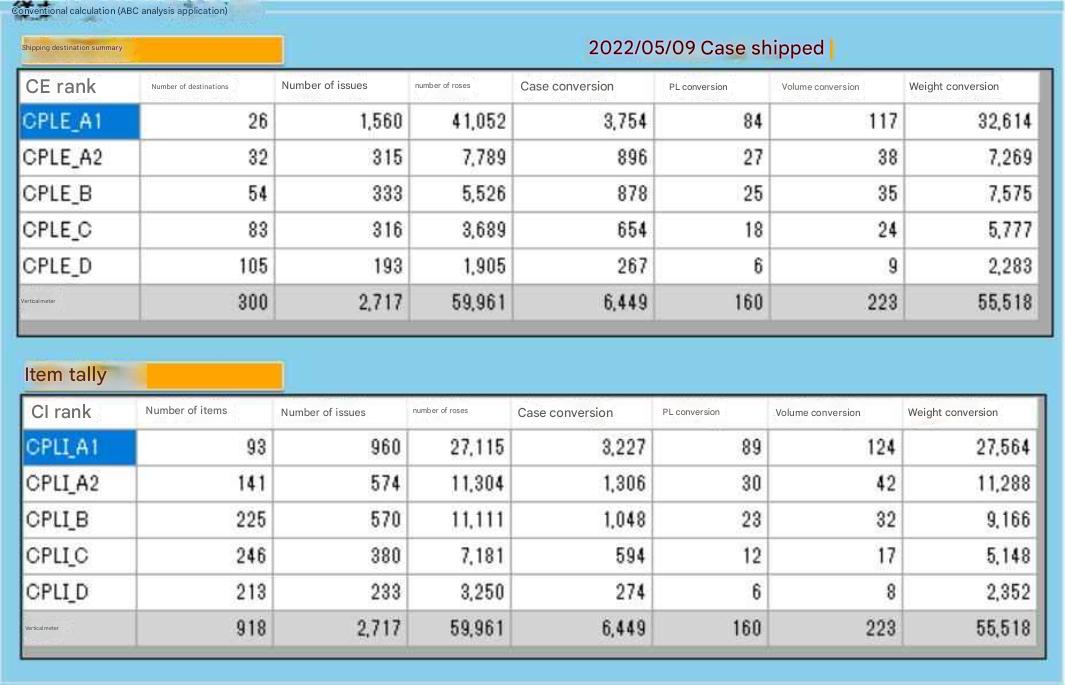
ケース出荷とバラ出荷は保管方法や作業方法が異なる。
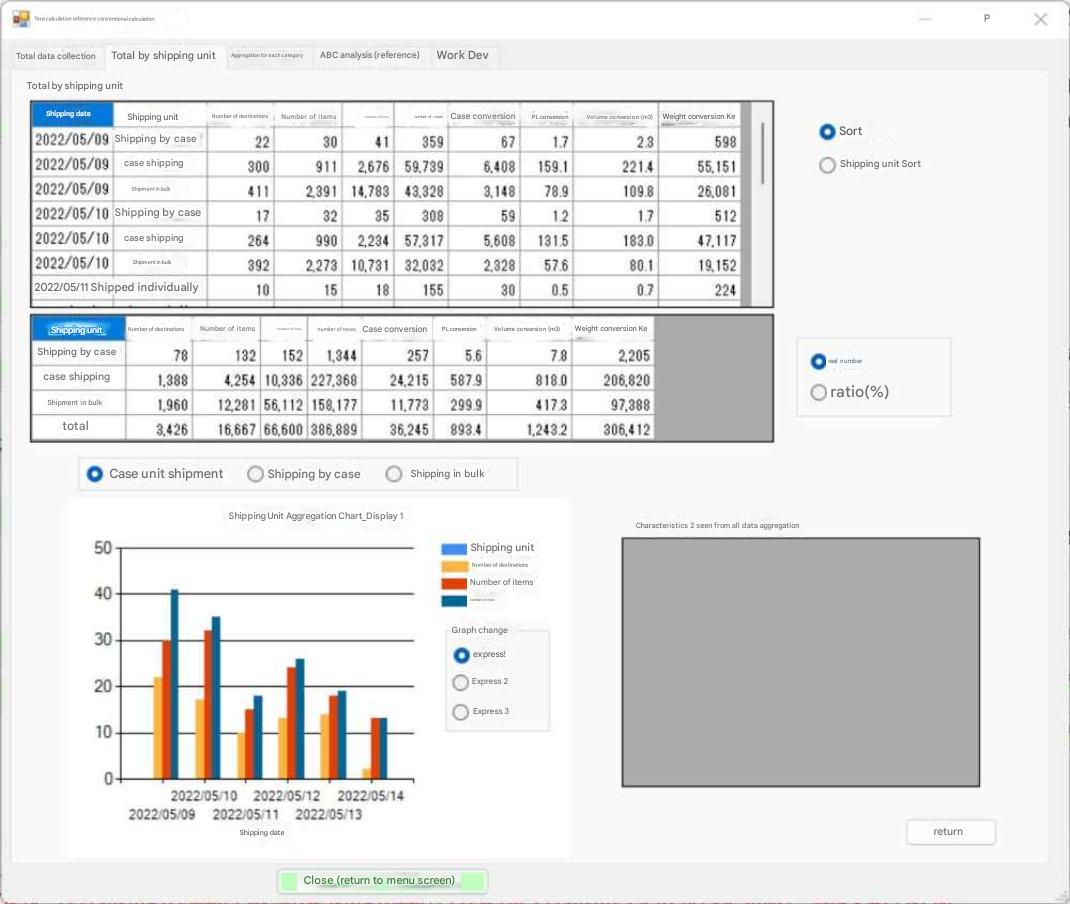
上記、全データ集計画面では、ケース出荷とバラ出荷の区分がされていないので、機器の割り付けは出来ない。システム設計としては参考データである。
|
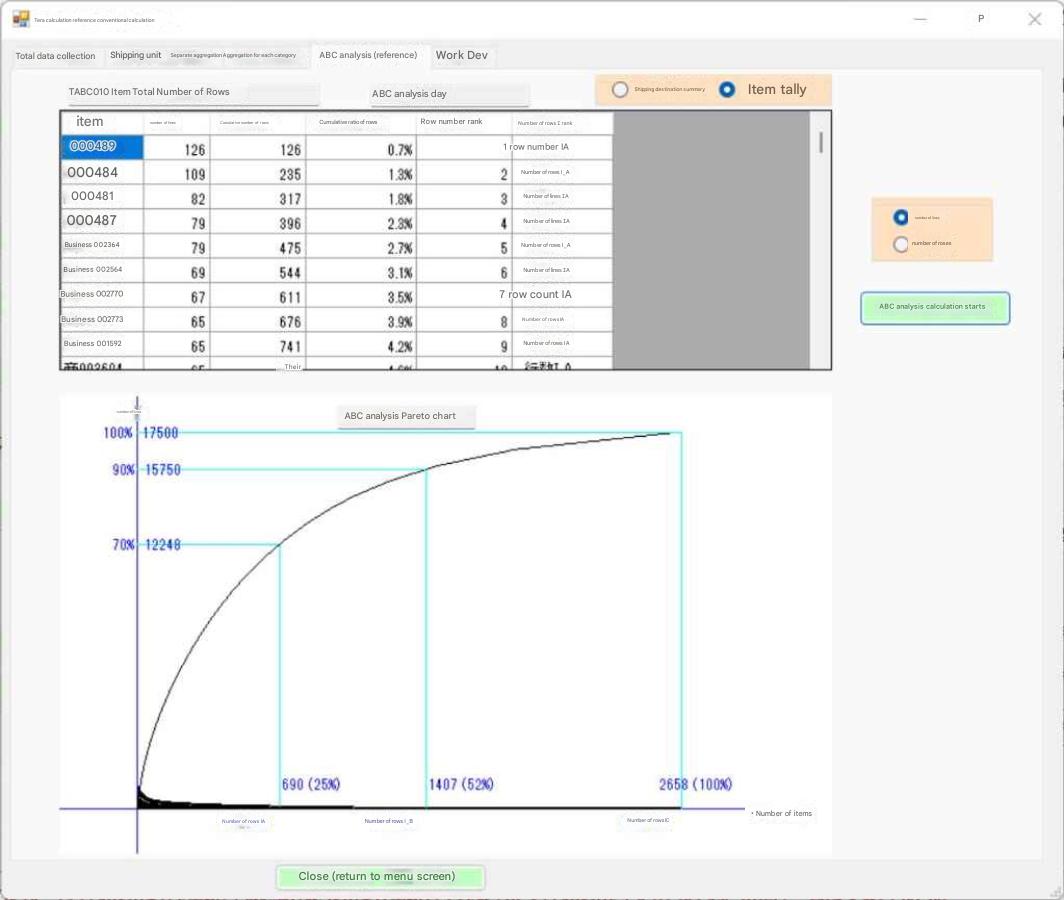
The "Shipping Data Summary" table on the left is a compilation of all shipping data by item, but also includes additional items not included in the shipping data, such as case, PL, volume, and weight conversions. The
"% Percentage" radio button indicates the percentage of each shipping date when all shipping data is 100%.
The total destinations and items in this shipping data are cumulative values for duplicate shipments on each day.
The shipping data includes 518 destinations and 4,594 items (as shown).
The "Graph" shows the shipping date, 2022/05/10 .
Display 1 shows destinations and items,
Display 2 shows the number of loose items ,
and Display 3 shows PL, volume, and weight conversions.
The "Characteristics as seen from the total data compilation"
shows a wide variety of case quantities, ranging from 1 to 120.
|