| EIQ table creation screen |
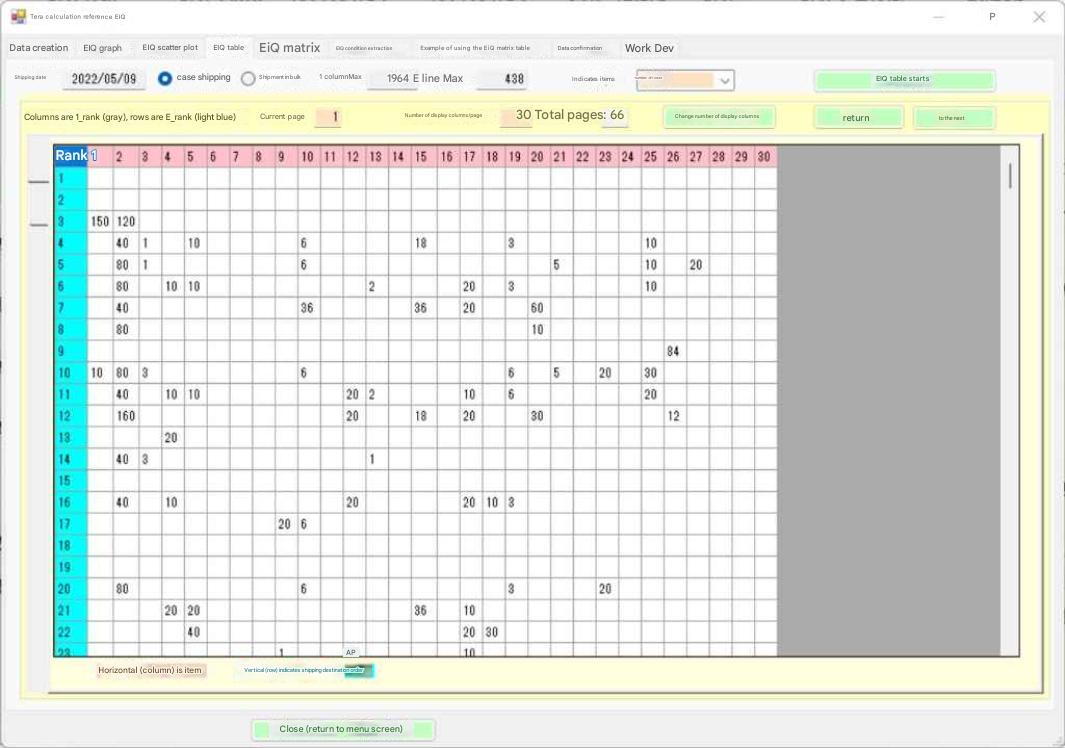 The table shows data for shipping date 2022/05/09, with items sorted by the number of items with the most items shipped, based on all shipping data. Shipping destinations 1 and 2 have not been shipped, so they are left blank. By scrolling, the figures for all 438 shipping destinations are displayed. There are 1,984 items, so they have been split across 66 pages, taking into account the display range and processing speed due to PC load. The table is 430 rows x 1,984 columns, and is unreadable to the human eye in its current state. Observation: In the table above, shipping destinations 1 and 2 are left blank. This blank space means that no shipments have been made to the top 1 and 2 shipping destinations. Perhaps there are urgent items being shipped at the lower levels, but shipping is not taking place on those days. This kind of intentional distribution of shipping dates is common at many distribution centers. |