This logistics equipment, known as SAS, was first sold in 1985, with over 700 units having been delivered.
In recent years, patent restrictions have been lifted, and logistics companies have begun selling it.
The equipment's features include
: 1. It has a sorting function that allows it to store 1,000 items when storing 1,000 cases, and can specify the shipping order for 1,000 destinations.
2. High-speed trolleys run along each shelf, allowing each unit to perform 50-60 inbound and outbound movements per hour.
This capacity
translates to 60 movements x 15 shelves = 900 inbound and outbound movements per hour for a 15-shelf SAS system.
For example,
if a worker picks loose items every 12 seconds on a flow shelving system,
the SAS outbound station can pick loose items 300 times per hour, with loose picking taking place in 5 seconds, for a total of 720 movements per hour.
3. It allows for a mix of case and loose shipments.
For example,
if a low-flow shipping destination receives one case of one item and three loose shipments of three items, totaling 15 loose items,
continuous mixed work is possible, eliminating the need to combine the cases and loose items.This
equipment enables the efficiency of low-flow shipping destinations and low-flow items, which are the most time-consuming and difficult to mechanize at distribution centers.
Calculation screen
In recent years, patent restrictions have been lifted, and logistics companies have begun selling it.
The equipment's features include
: 1. It has a sorting function that allows it to store 1,000 items when storing 1,000 cases, and can specify the shipping order for 1,000 destinations.
2. High-speed trolleys run along each shelf, allowing each unit to perform 50-60 inbound and outbound movements per hour.
This capacity
translates to 60 movements x 15 shelves = 900 inbound and outbound movements per hour for a 15-shelf SAS system.
For example,
if a worker picks loose items every 12 seconds on a flow shelving system,
the SAS outbound station can pick loose items 300 times per hour, with loose picking taking place in 5 seconds, for a total of 720 movements per hour.
3. It allows for a mix of case and loose shipments.
For example,
if a low-flow shipping destination receives one case of one item and three loose shipments of three items, totaling 15 loose items,
continuous mixed work is possible, eliminating the need to combine the cases and loose items.This
equipment enables the efficiency of low-flow shipping destinations and low-flow items, which are the most time-consuming and difficult to mechanize at distribution centers.
| The low-flow destinations and items in the red box below are placed in the automated case warehouse and shipped mixed per destination. |
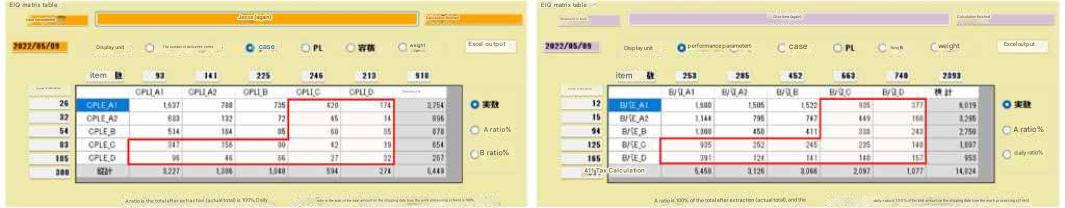 |
Calculation screen
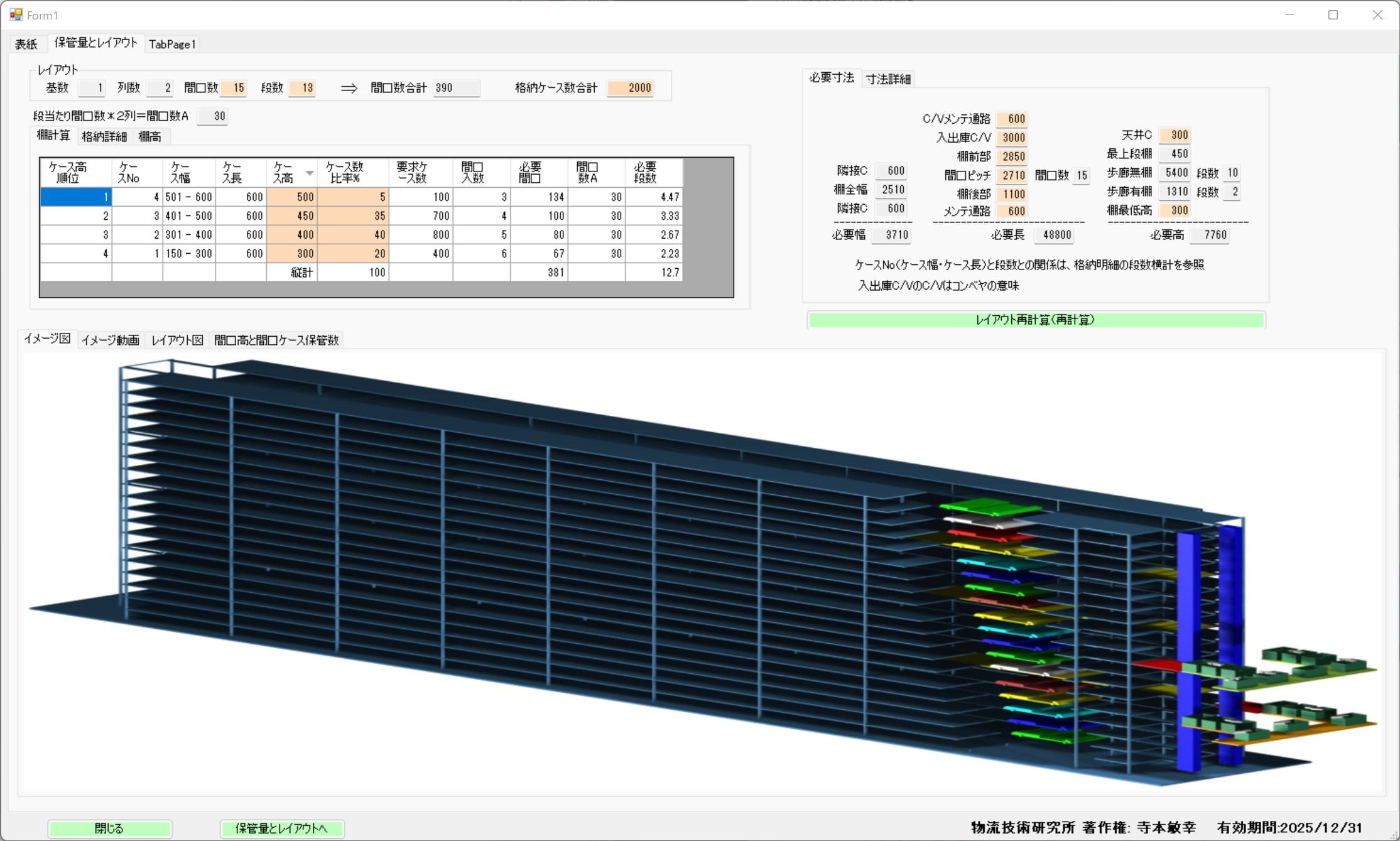 |
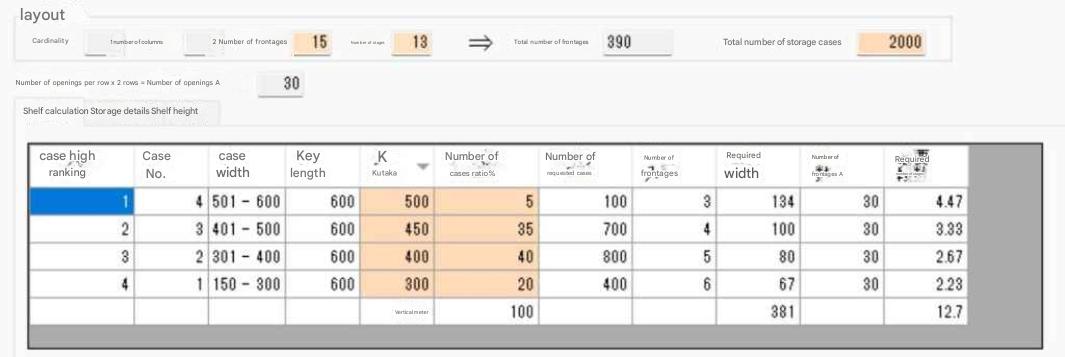
| Case packaging and number of items stored |
 |
|
| Operation of the automated case warehouse |
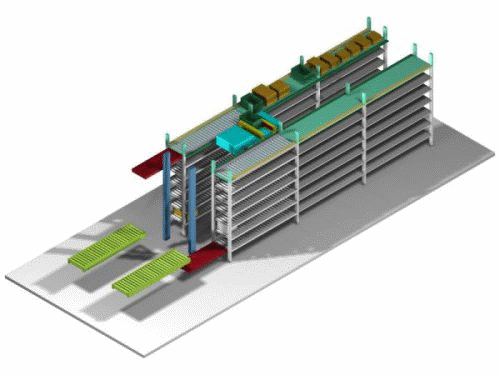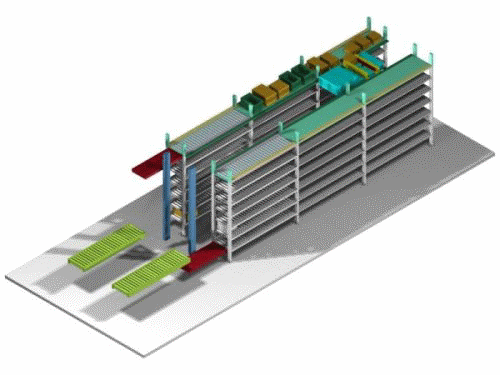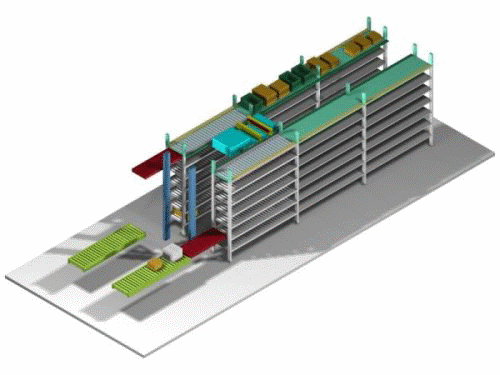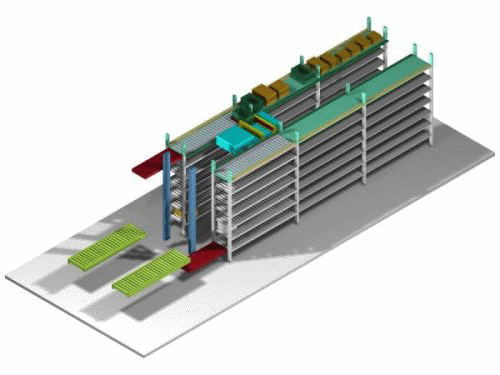 |
The incoming case is transferred from the in-storage conveyor, transported to the shelf entrance, stored on the shelf , moved to the shelf entrance where the outgoing case is located, the case is transferred and transported, the case is lowered onto the in-storage conveyor, and then transferred to the outgoing shelf conveyor by a vertical transport machine.The above in-storage and outgoing processes can be performed 50-60 times per hour. |
| Flat layout |
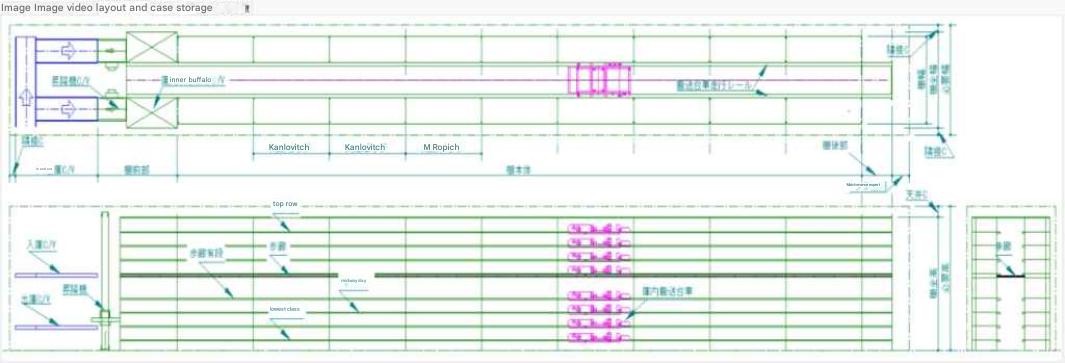
The case shelves can be fitted with inbound and outbound conveyors at the front and rear (the layout above is only at the front).
Walkways are installed at 2000mm intervals in height, allowing for removal of the shelves in the event of a breakdown.
Calculations are based on the assumption that there is a virtual floor every 5m above the top shelf.
Walkways are installed at 2000mm intervals in height, allowing for removal of the shelves in the event of a breakdown.
Calculations are based on the assumption that there is a virtual floor every 5m above the top shelf.
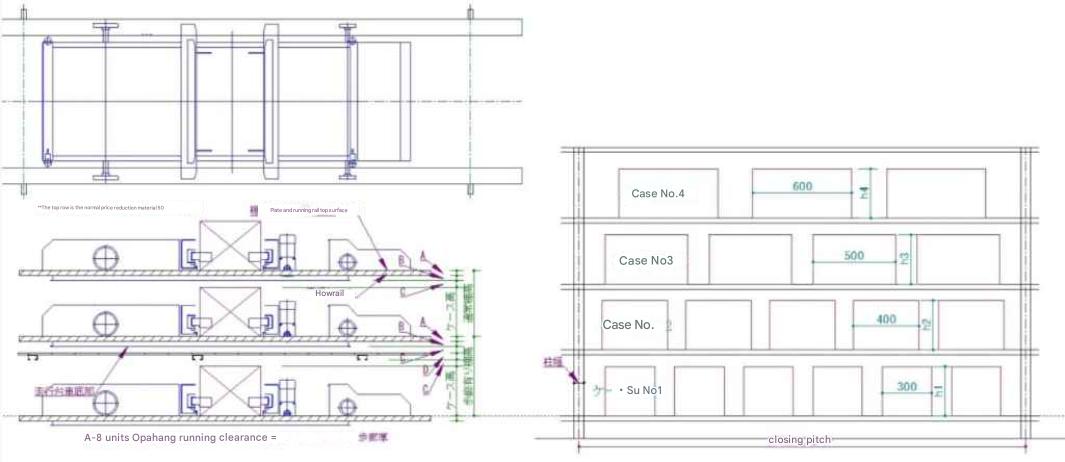
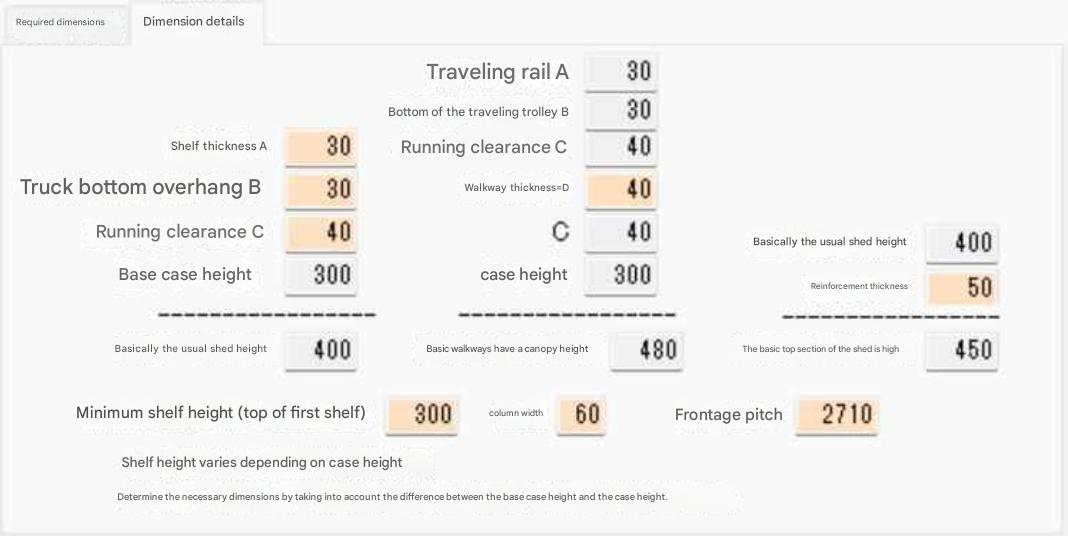
| Traveling cart and shelf opening height and opening width and number of cases stored Opening pitch: 2710 mm, number of cases stored per opening: 6 cases for 300 mm wide, 5 cases for 400 mm wide, 4 cases for 500 mm wide, 3 cases for 600 mm wide |
 |
| Dimensions can be changed |
 |
The running carriage is designed to overhang below the rails, so be careful of the dimensions of the entrance with and without a walkway. Tera settings can be changed. |