| Shipping work space calculation screen | |||
|
|
|||
 |
|||
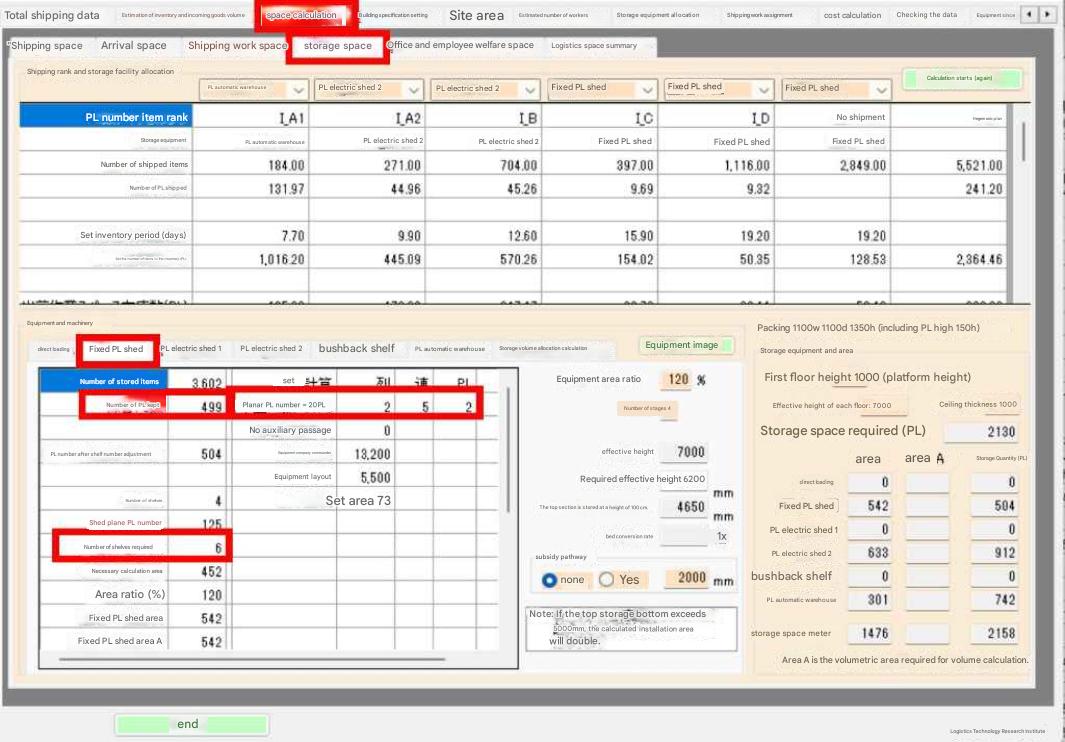
Section 1. Calculation of storage space areaCase shipping items are shipped directly from the storage space, so the total inventory is storage space inventory. Bulk shipping items are replenished from the storage space to the shipping work space and then picked and shipped from the shipping work space (flow shelves or medium-volume shelves). A certain amount of bulk shipping items is stored on these flow shelves and medium-volume shelves. Therefore, the inventory of bulk shipping items in the storage space is the total inventory of bulk shipping items - shipping work space inventory. Storage Space and Shipping Work Space Quantity Allocation Calculation The focus is on calculating the number of loose D- rank items that are completed only on the shipping work space shelves and are not stored on the storage space shelves. Total number of loose D- rank items = 2847 Total volume of loose D- rank items = 118 Loose D -rank shelf volume = 241 Loose shelf volume ratio = 204 % Number of items completed on loose shelves 2847 = Int (Total number of loose D- rank items * ((Loose shelf volume ratio / 100 ) * 0.6 ) + 0.5 ) Of the 3082 loose shipping item rank D items (including inventory not shipped), 2847 items are stored on the shipping work space shelves and not on the storage space shelves. The number of loose shipping item rank D products stored on the storage space shelves is 235 items. Another point to note is that the shelf calculation for the shipping work space is based on volumetric conversion, while the shelf calculation for the storage space is based on product liability conversion. The number of pallets stored cannot be calculated accurately using volumetric conversion. This is why the product liability loading number of cases (stack module) is set for each item in the shipping data items. Shipping Rank and Storage Facility Allocation: |
| Shipping work space calculation screen | |||
|
|
|||
 |
|||
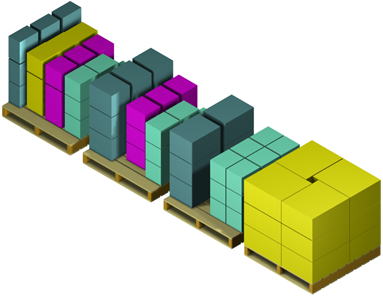 |
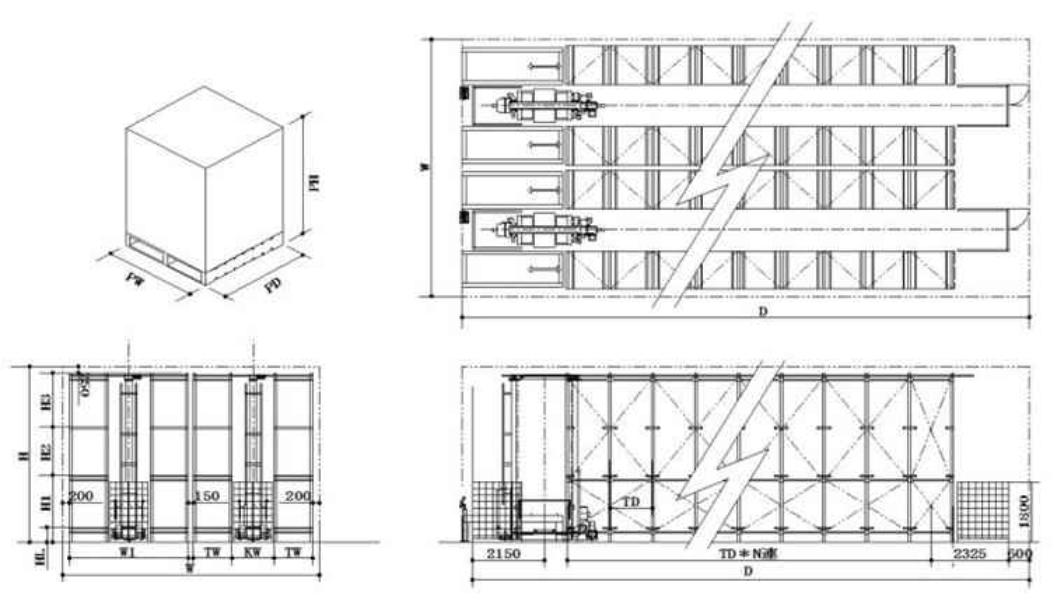
: For all calculations oftera1100W1100D 1350H (including PL height 150 mm). In terms of storage packaging, placing one item on one pallet is called single-load storage (single-load PL ), while placing two items on one pallet is called double -mixed storage ( double -mixed PL ). Mixed storage is classified as mixed by writing the number of mixed items at the beginning of the name. Products on a pallet are stacked vertically (called vertical stacking) to prevent mixing with other products. For this reason, mixed PL has lower storage efficiency than single-load. PL fixed shelves are used in most distribution centers, and because pallets are supported by beams (cross beams), loading aisles can be installed between the shelves ( called dual shelving ), allowing loading and unloading of products on any pallet at any time. |
Unlike direct stacking, products are not placed on top of other products, preventing damage to products, and products are lined up in an orderly fashion on pallets, facilitating location management (a system that links products with shelf addresses to facilitate accurate storage and retrieval).
Shelves are anchored 100-200mm away from the building ( varies depending on height and proximity to the building) and secured with anchors (floor stoppers) to prevent products and equipment from coming into contact with the building during loading and unloading, providing a distance (called clearance) to prevent contact between the building and shelves during an earthquake.
The clearance between stored goods is 100mm between the shelf supports and cross beams. Both pallet loads are 100mm .
1. With the shelving installation section A and the shelf auxiliary aisle B as the calculation units, the shelves in section A are 2 rows * 5 rows * 3 rows * 2 PL = 60 PL , so the area required to store 13.1 m * 5 m = 65.5 m2, and when addition is selected for the aisle in section B, 5 m * 2 m
= 10 m2 is added to the calculation. However, since one shelf is made up
of 2 PL * 3 rows, it is an integer multiple of 6 PL, so if there is 130 PL, it is calculated as 132 PL. For example, if 132 PL needs to be stored, then 132 PL / 6 PL = 2 shelves, and since section A is made up of 10 shelves, an installation
area of 2.2 times the area , 65.5 m2 * 2.2 = 67.7 m2, is required. The shelf auxiliary aisle requires 2.2 times the area * 10 m2 = 22 m2 .
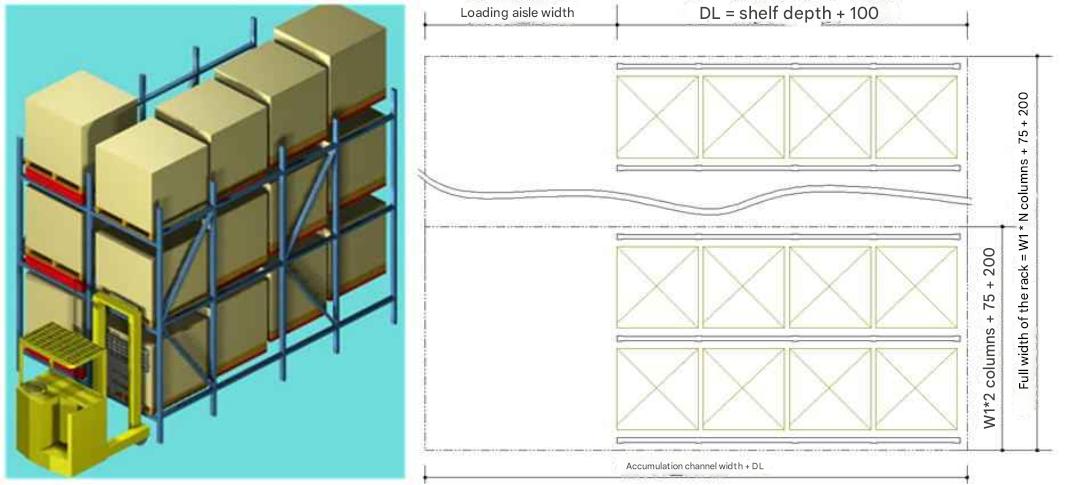
プッシュバック棚 |
 |
 |
PL electric trolleys are a type of equipment that has been widely installed. PL electric shelving units share two aisles by placing PL fixed shelves on the electric trolley and moving the electric trolley shelves. This reduces the number of aisles (to one), thereby reducing the shelf installation area. When electric shelving units were first commercialized, track rails had to be embedded in the floor, but recently, railless electric shelving units have become more common. Railless electric shelving units do not require floor construction, which is one of the reasons for their increasing installation. The calculation method is the same as for PL fixed shelving units. Note that the electric trolley is 200-250 mm high, so the height dimension of the PL shelf on the electric trolley is 200-250 mm higher than the PL fixed shelf. A control panel 400 mm high is installed on one side of the electric trolley in the connecting direction, and the height of the PL fixed shelf in the connecting direction is 400 mm higher. Since the shelves carry a large load and tend to deflect, attention must be paid to floor strength. |
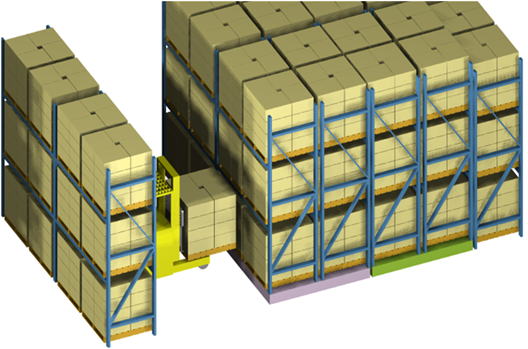 |
Item 4 PL Electric Shelving Unit 2 PL Electric Shelving Unit 2 has two PL electric shelves placed between PL fixed shelves, making it possible to handle cargo in one aisle where three aisles would normally be required. |
In progress
| PL自動倉庫 |
 |
写真説明 |
その他設備 |
| 写真説明 |
| 写真説明 |