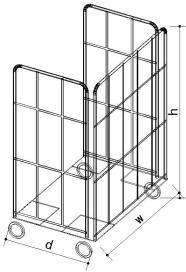
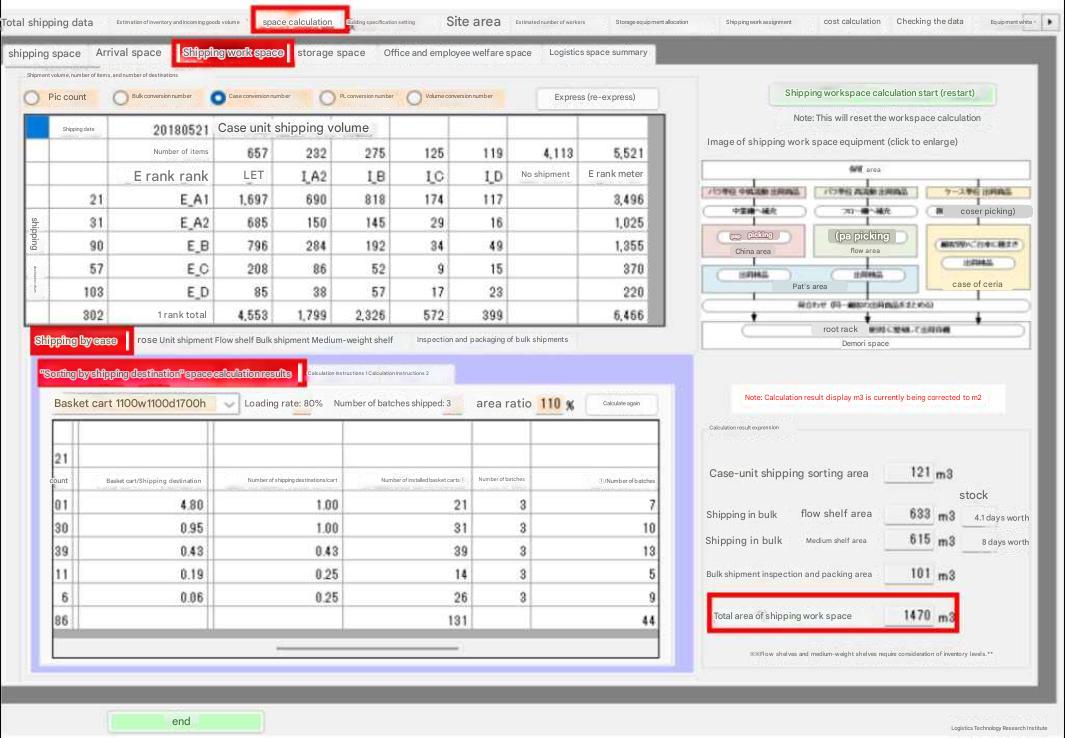
Item 1. Calculation of shipping work space area
| Because case shipments and bulk shipments have different work methods,
they have different work areas and calculation methods. Separate calculations
for case shipments and bulk shipments are made to clearly define the shipping
work space and improve calculation accuracy. Case shipments are removed
from the warehouse on an item-by-item basis and sorted by destination.
Bulk shipments are removed from the warehouse on an item-by-item basis
and stored on flow or medium-weight storage shelves, from which they are
picked by destination. The shipping work space also includes space for inspection and packaging. Tera Calculation 2 calculates that inspection of case shipments is performed during sorting, while inspection and packaging for bulk shipments are performed in a designated inspection and packaging area. If you select inspection during picking, which is not adopted in Tera Calculation 2, an inspection area is not required, and the inspection and packaging area can be used as a space for cardboard packaging for small-lot collection destinations and individual shipments that cannot be shipped in shipping containers. Section 2: Processing items not in shipping data The calculation procedure involves determining the number of shelf openings
and shelf opening volume (determined by the number of openings per shelf)
and then looking at the shelf inventory days. If you want to increase the
shelf inventory days, reduce the number of openings per shelf (increase
the opening volume), and if you want to decrease the shelf inventory days,
increase the number of openings per shelf (decrease the opening volume),
and determine the shelf specifications and number of shelves. The more
openings per shelf, the fewer the number of shelves, and if it is fewer,
the number of shelves will increase. Section 3: Case shipments are sorted into basket carts (shipping destinations). |
|
2. Based on the calculation in 1 , calculate the number of basket carts per shipping destination for each shipping destination rank . Calculate the volume/number of shipping destinations by rank, and if the value is 0.5 or more, use one cart per shipping destination, if it is 0.5 to 0.4 or more , use one cart per two shipping destinations, if it is 0.4 to 0.3 or more , use one cart per three shipping destinations , if it is 0.3 to 0.2 or more , use one cart per four shipping destinations , and if it is 0.2 or less, use one cart per five shipping destinations. Determine the calculation conditions and calculate the number of basket carts to set up for sorting. 3. Divide the calculation in 2 by 3 batches to calculate the sorting area per batch. 4. Multiply the value calculated in 3 by the area multiplier. Item 4 Flow Shelf |
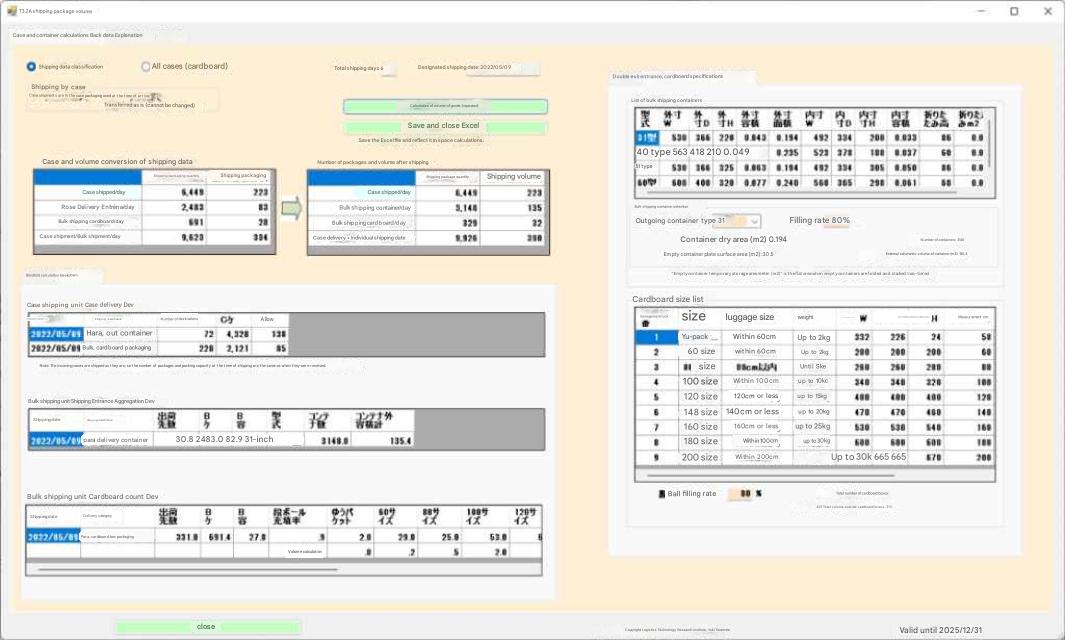 |
Bulk shipments are picked. 1. Specify flow shelving or medium-weight shelving depending on the shipping destination rank. 1-1. For bulk shipment rank A1, specify flow shelving and set the flow shelving specifications. Shelf width = 2400, shelf depth = 2050, shelf height = 2114, number of shelves = 4, number of openings (per shelf) = 5 1-2. Calculating the floor area per flow shelving shelf: Area per shelf = Shelf width * Shelf depth / 1000 ^ 2 Pic aisle area per shelf = Shelf width * 800 / 1000 ^ 2 Replenishment aisle area per shelf = Shelf width * 800 / 1000 ^ 2 Calculating floor area per shelf = Area per shelf + Pic aisle area per shelf + Replenishment aisle area per shelf |
1-3. ' Flow shelf Frontage volume calculation per
shelfShelf width effective dimension A = shelf width – 60Frontage
effective width = ( shelf width effective dimension - ( number of frontages per shelf ) * 20 + 20 ) / number of frontages per shelf'Frontage gap 20 is number of frontages + 1Frontage effective depth = shelf depthFrontage effective height = (shelf height - ( 80 * number of shelves + 20)) / number of shelves'80 is material thickness, 20 is first shelf lossFrontage effective volume = ( frontage effective width * frontage effective depth * frontage effective height ) / 1000 ^ 3Frontage calculated volume = frontage effective volume * ( shelf_frontage volume filling rate / 100 ) Calculated volume per shelf = frontage calculated volume * number of shelves * number of frontages per shelf1-4. Tera setting specifies flow shelves for A1 and A2 ranks.
Item 5. Medium-Duty Shelves |
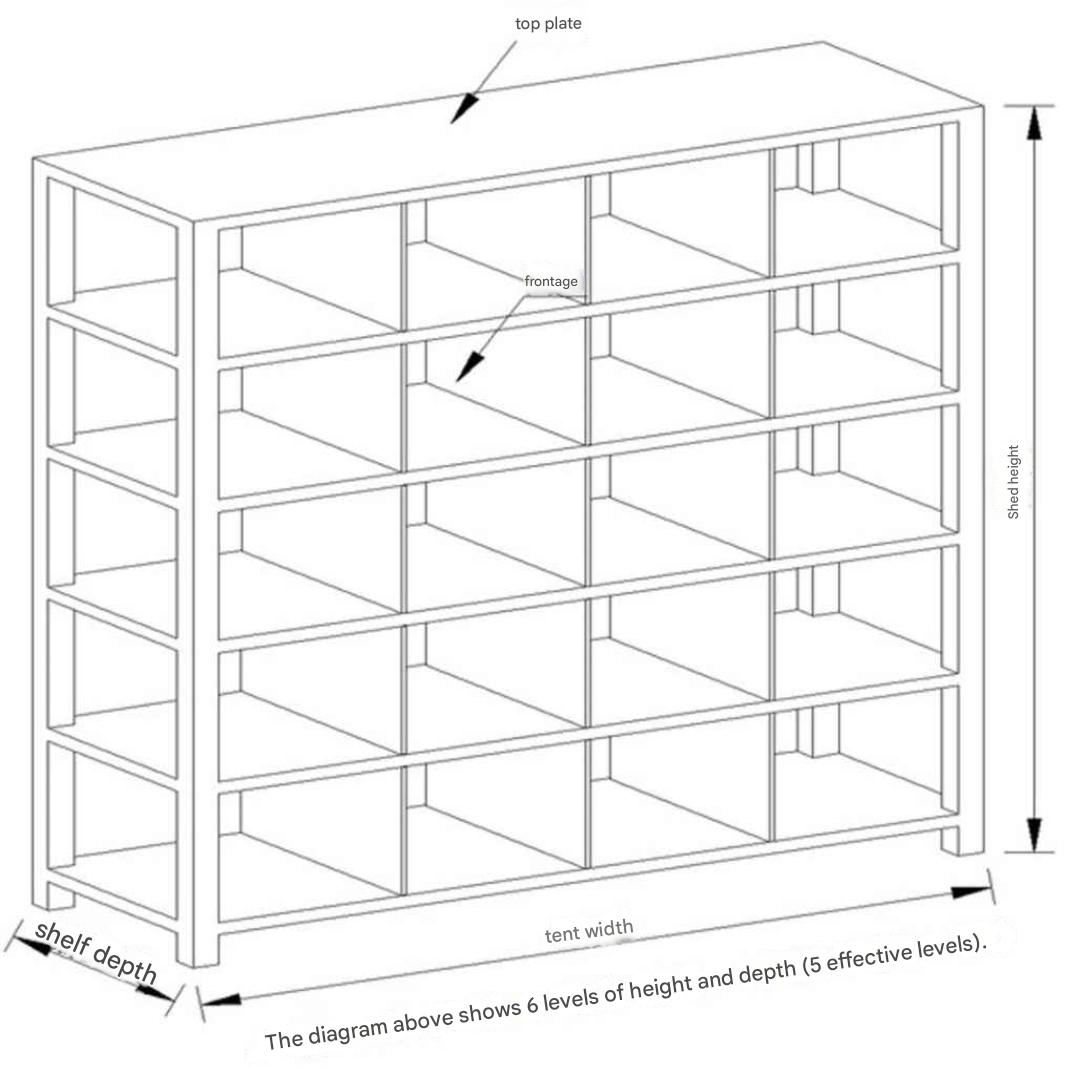 |
2-1. For bulk shipping rank B , specify medium-duty shelves and set the specifications for the medium-duty shelves. 2-2 . Medium-duty shelf Calculating the floor area per shelf Area per shelf = Shelf width * Shelf depth / 1000 ^ 2 Pic per shelf Aisle area = ( Shelf width * 600) / 1000 ^ 2 Calculating floor area per shelf = Area per shelf + Pic per shelf Aisle area 2-3. ' Calculation of frontage volume per shelf Effective shelf width = shelf width – 60 Effective frontage width = Int(( effective shelf width - number of frontages per shelf * 10) / number of frontages per shelf + 0.5) ' Frontage gap 10 is number of frontages + 1 Effective frontage depth = shelf depth Effective frontage height = Int(( shelf height - (130 + number of shelves * 40)) / number of shelves + 0.5) ' The first shelf is included in 130 Effective frontage volume = ( effective frontage width * effective frontage depth * effective frontage height ) / (1000 ^ 3) Calculated frontage volume = effective frontage volume * (shelf_frontage volume filling rate / 100) Calculated volume per shelf = calculated frontage volume * number of shelves * number of frontages per shelf 2 - 4. Tera settings specify medium-weight shelves for B , C , and D ranks. Int (*** + 0.5 ) means that the decimal point of the calculated number is rounded down to the nearest 4. The loose shelf summary table displays the calculation process and results based on the above formula.
|
Section 6: Inspection and packaging of bulk shipments
All picked loose products are placed in shipping containers and transported to the inspection and packing area.
(Products shipped in cases are inspected when sorted into cases.) Inspection. The area of the packing area is:
1. 8.252 loose products per hour = 26,449 loose products shipped / 31% of peak volume
2. Total loose product processing time 24,756 = 8.252 loose products per hour / 3 seconds inspection time per loose product
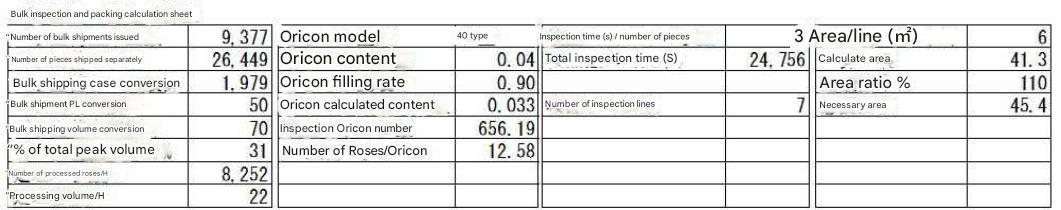
3. Number of inspection lines: 7 = Total processing time for individual items: 24,756 / 3,600 seconds (to process in one hour)
6. Required area: 45.4 = Number of inspection lines: 7 * Area per line: 6 m2 * Area multiplier: 110% The area per line ( 6 m2) varies
depending on the size of the shipping container .
Shipping space area multiplier
Since there are multiple tasks with different work contents, the shipping space area multiplier is set for each task.
mentioned that when calculating bulk shipments, shelf specifications are
determined by checking the shelf inventory days, but the "Inventory"
flow shelf in this table, 3.5 days ' worth, and medium-weight shelf, 12.8 days' worth, are the inventory days of the shelves we are focusing on.This workspace inventory quantity is Storage space inventory = Total inventory
- Workspace inventory, and affects storage space inventory.
Section 7 Inspection and Packing Bulk Pic Flow Chart |
| Tera Calculation 2: Distribution center size calculation assumes inspection-less operation. The operation that can realize inspection-less operation is explained below. |
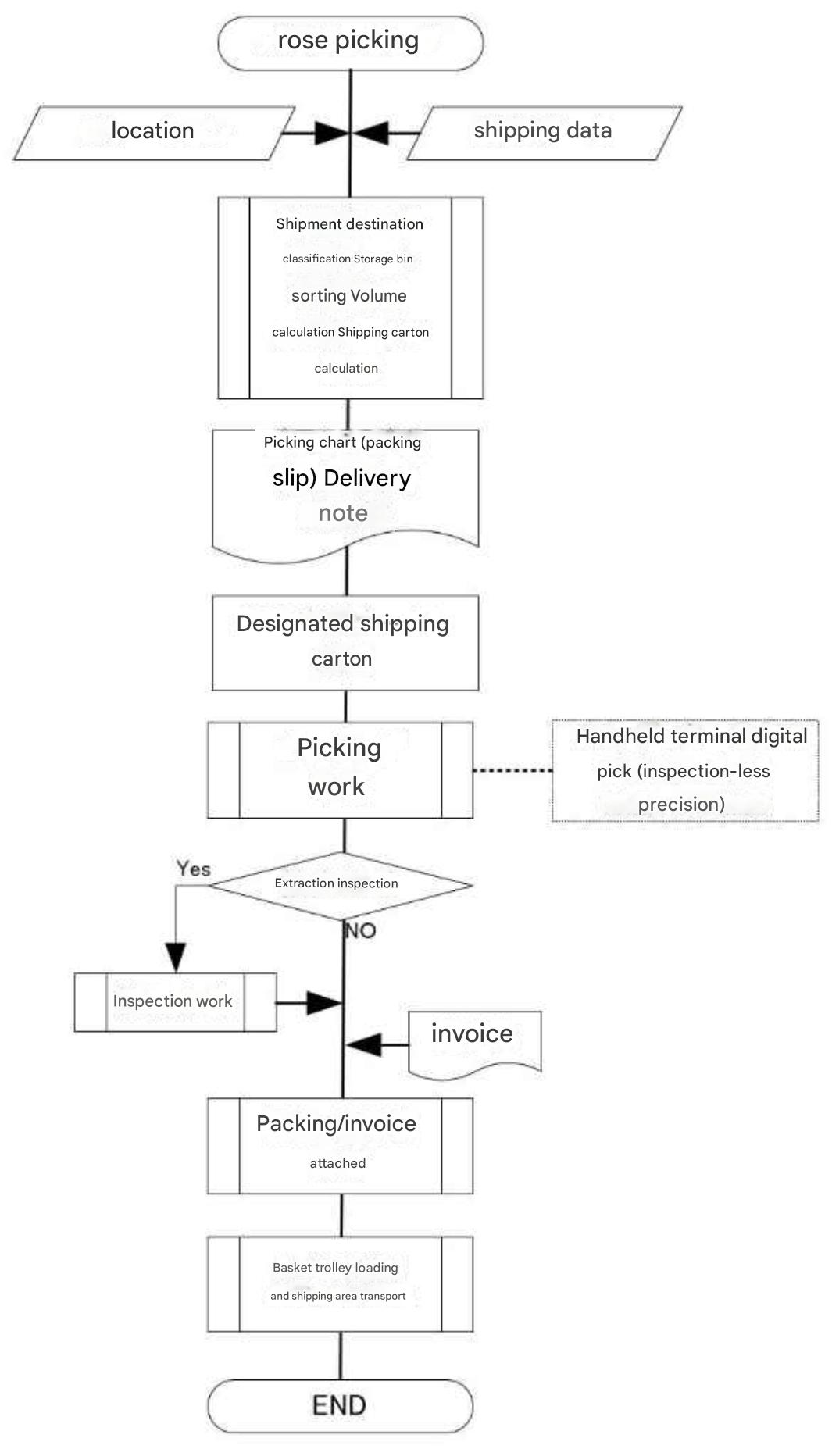 |
1. Information processing before picking, linking shipping data records with location management shelf numbers, and tallying and sorting shelf numbers by destination. Calculating volume by destination and allocating optimal shipping cartons. 2. Issuing a picking chart (packing details, not used during picking) and delivery note. 3. Packing designated shipping cartons (folded). 4. Starting picking using a handheld terminal or digital picking (requires an information system and operational management to guarantee no inspection required). 5. For cartons designated for sample inspection, restart from step 6 after shipping inspection. 6. Scan the code on the picking chart and issue a shipping label. 7. Place the picking chart and delivery note into the shipping carton, seal it, and then attach the shipping label to the shipping carton. (Packaging is not required for shipping containers.) 8. Load the designated shipping carton onto a cart. 9. Repeating steps 1-8, confirming that picking has been completed at the designated shipping destination, and transporting the cart to the shipping area without inspection requires volume management, information processing for shipping carton allocation, and advanced work (operation) management. |