| Item 7. Truck Loading Methods |
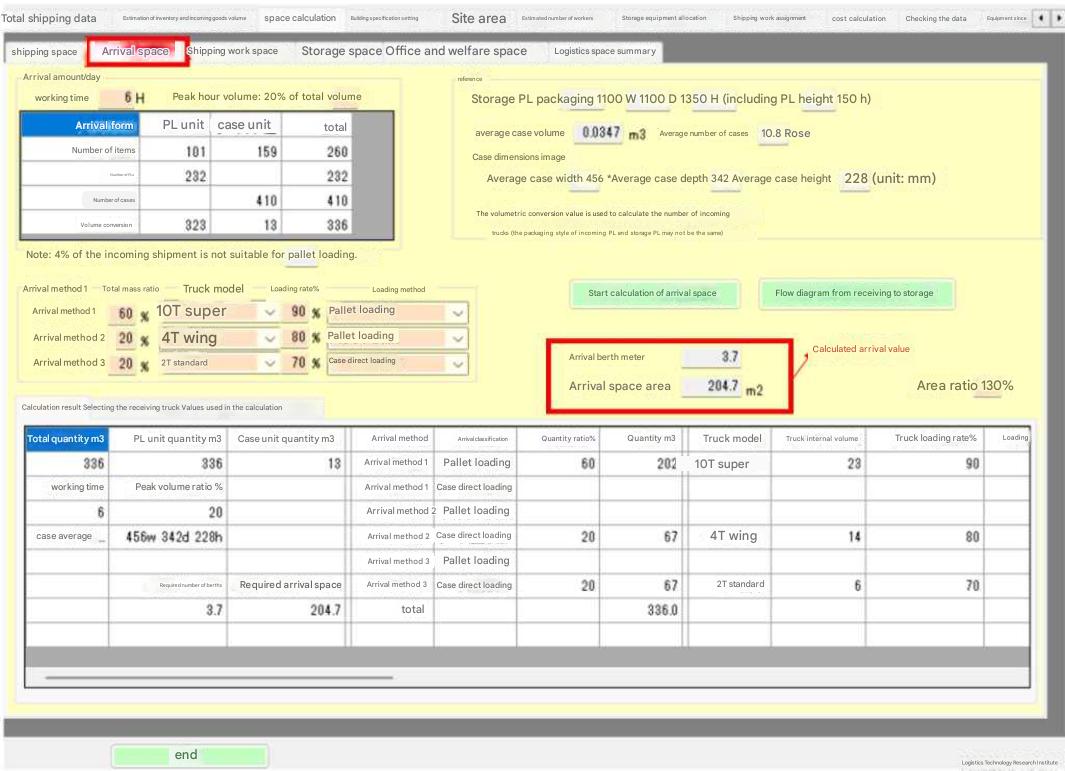
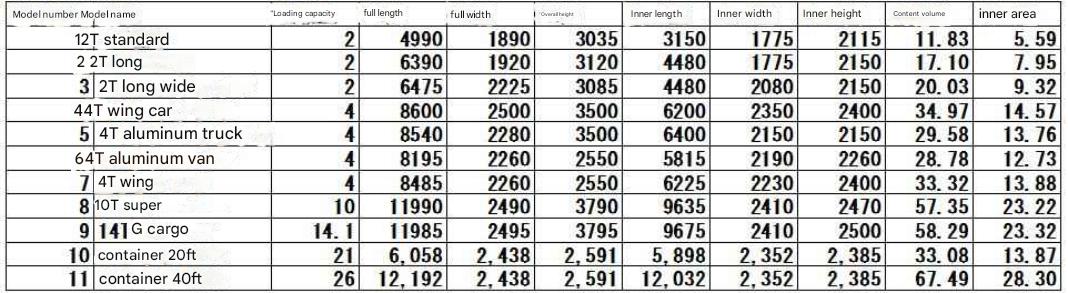
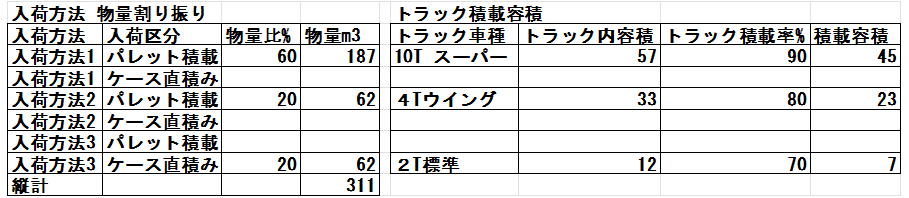
There are two types of loading methods: pallet loading and direct case loading. Pallet loading is ideal as it allows for quick loading and unloading from trucks, but for vehicles with a load capacity of less than 4 tons, the loading rate of pallet loading is low, so direct case loading is common. Pallet loading is used on large trucks that can load two pallets per bed width, but there is a loss of two pallet thicknesses (150 mm x 2) relative to the height of the truck bed.
Large trucks for long-distance transport often use direct case loading to avoid this loss in pallet thickness.
Direct case loading is calculated using the case volume. Pallet loading is calculated using the direct case loading calculation * ((number of loaded pallets * 150) / truck bed height).
Section 8. Incorporation of Air Transportation Equipment into Calculations
|
When loading on pallets, the receiving berth area is the shipping waiting area + the temporary storage area of returned empty pallets. When loading directly onto cases, the calculation is based on the temporary storage area of returned empty pallets = 0.
Item 9. Number of Arrival Berths
|
An inbound berth is the opening (also called a dock) of a distribution center where inbound trucks need to unload their cargo, and the number of inbound berths is the number of docks required during peak hours ( 1 hour). Calculated by dividing the cumulative truck arrival time ( minutes ) per hour by 60 minutes. Truck arrival time is preset for each vehicle type. (See Inbound Space Calculation.xlsx )
Section 10: Receiving Space Area Ratio
|
The calculation of the receiving space area does not take into account
gaps between waiting products, aisles for workers to load and unload, work
and office space, etc. The calculation of the number of receiving
berths does not take into account inspection time, time to process slips,
delays caused by interference between receiving and shipping trucks, etc.
These required times are taken into account using the area multiplier.
|